What Is a Credit Score and Why Does It Matter in 2025?
In today’s financial landscape, a credit score is more than just a number. It is a critical metric that can influence multiple aspects of your life — from loan approvals to housing applications, and in some cases, even employment opportunities.
This article explains what a credit score is, how it is calculated, and why it continues to play a central role in personal finance.
What Is a Credit Score?
A credit score is a three-digit number that reflects an individual’s creditworthiness. It represents the likelihood that a person will repay borrowed money on time.
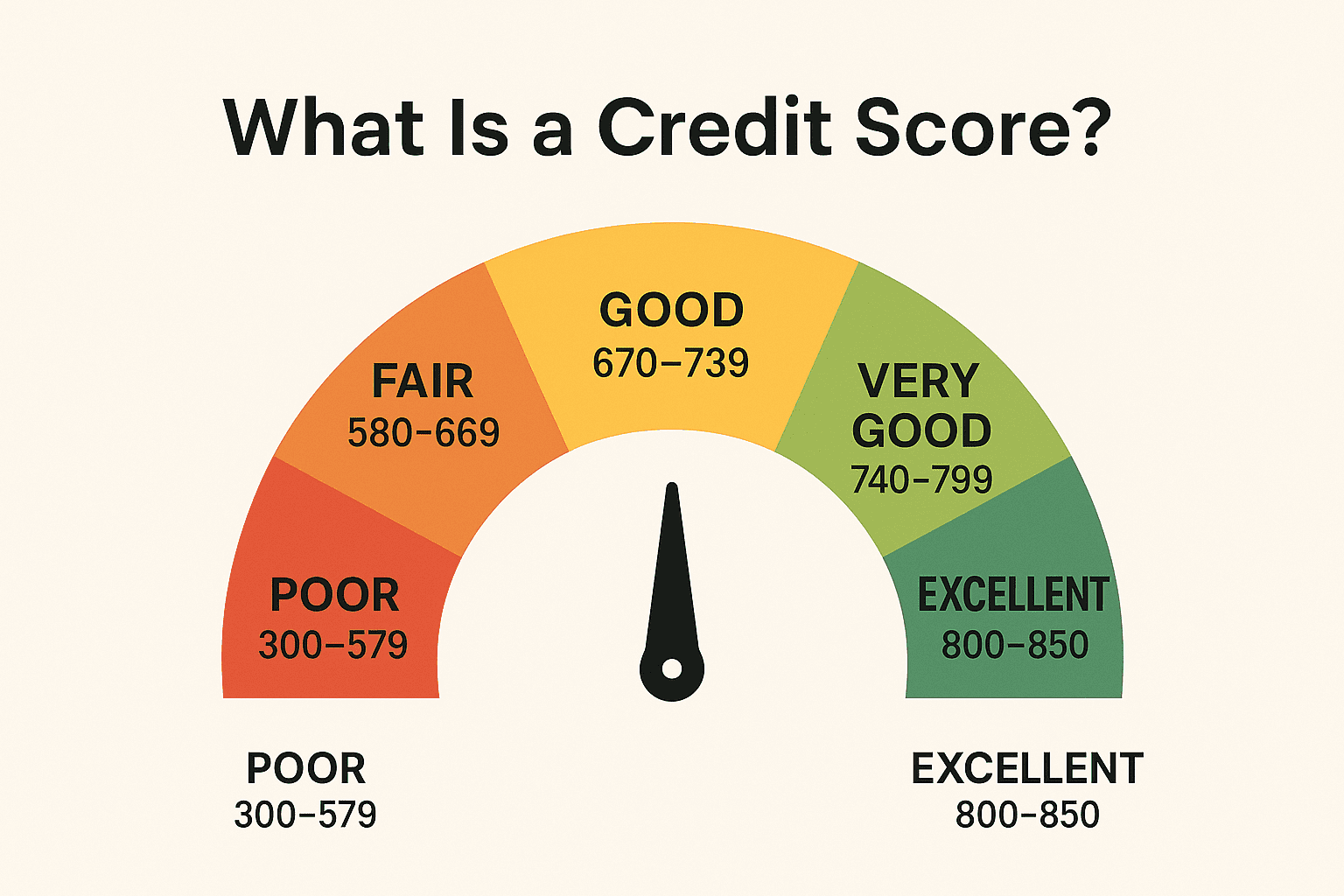
In the United States, credit scores generally range from 300 to 850. The higher the score, the more favorably lenders and other institutions view the individual.
| Score Range | Classification |
|---|---|
| 800–850 | Excellent |
| 740–799 | Very Good |
| 670–739 | Good |
| 580–669 | Fair |
| 300–579 | Poor |
A score above 700 is typically considered good, while anything under 600 may limit access to loans or result in higher interest rates.
How Is a Credit Score Calculated?
Credit scores are calculated using several weighted factors:
- Payment History (35%): Whether bills and credit obligations are paid on time.
- Credit Utilization (30%): The percentage of available credit that is being used.
- Length of Credit History (15%): The average age of credit accounts.
- Credit Mix (10%): The variety of credit types held (e.g., credit cards, installment loans).
- New Credit (10%): Recent applications for new credit lines or accounts.
Each of these components provides insight into how a person manages debt and credit.
Why Does a Credit Score Matter?
A credit score directly impacts many financial decisions and opportunities. For example:
- Loan approvals and credit card applications often depend on a minimum score threshold.
- The interest rate offered by a lender can vary significantly based on the applicant’s score.
- Landlords may request a credit report before approving a rental application.
- Utility companies and mobile service providers may require security deposits based on credit history.
- In certain sectors, employers may include a credit check in their hiring process.
In essence, a strong credit score can translate to better financial terms, lower costs, and broader access to services.
What Happens If You Do Not Have a Credit Score?
Individuals with no prior credit activity may have no credit score at all. This is common among younger adults or those who have intentionally avoided credit.
However, having no score can be as limiting as having a poor one. Lenders and landlords may interpret a lack of credit history as a potential risk, making approvals more difficult.
Conclusion
A credit score is not simply a banking tool — it is a financial signal used across many aspects of modern life. Understanding how it works and taking steps to manage it responsibly can open doors to greater financial flexibility and stability.
CreditFixerUSA.com offers practical guidance and reliable information for individuals looking to improve their credit.
Stay informed. Take control. Build the credit profile you deserve.